
从网络搜索结果中解析数据往往是一件麻烦事。但如果有一种方法能让这一艰苦的过程变得轻而易举呢?让我们尝试一下 OpenAI 的新人工智能模型吧。
Hilman Ramadhan
我一直很惊讶 OpenAI 的 chatGPT 在回答问题方面的表现,以及 Dall-e 3 制作精美图片的能力。现在,有了新的模型,让我们看看人工智能如何处理我们的网络搜索任务,特别是解析搜索引擎结果。我们都知道,从原始 HTML 中提取解析数据通常会很麻烦。但是,如果有一种方法可以将这一艰苦的过程变得轻而易举呢?
最近(2023 年 11 月),OpenAI 团队召开了 首次开发者大会:DevDay(欢迎先观看)。其中一个令人兴奋的公告是 GPT-4 的更大的上下文窗口。新的 GPT-4 Turbo 型号功能更强、更便宜,而且支持 128K 上下文窗口。
封面插图:OpenAI 的 AI 网络爬虫。
我们的小实验
在过去,我们比较了一些开源和付费 LLM 将纯文本数据转换成简单格式的能力,并开发了一个人工智能驱动的解析器。
这一次,我们将提升挑战的难度。
- 直接从原始 HTML 数据中抓取。
- 转换成我们需要的特定 JSON 格式。
- 只用很少的开发时间。
我们的目标
- 抓取一个结构良好的网站(作为热身)。
- 从 Google 搜索结果页面返回自然搜索结果(organic results)。
- 从谷歌 SERP 返回 “人们还问(相关问题)”部分。
- 从 Google MAPS 返回当地搜索结果。
请记住,人工智能的任务只是解析原始 HTML 数据,而不是自己进行
网页抓取。
TLDR(简而言之)
如果您不想阅读整篇文章,下面是我们使用 OpenAI API(新 GPT-4)模型进行网页抓取实验的利弊总结:
优点
- 新模型
gpt-4-1106-preview能够完美地抓取原始HTML数据。更大的令牌窗口使得只需传递原始HTML数据即可进行抓取。 OpenAI的函数调用可以准确返回我们需要的响应格式。- OpenAI 的
多函数调用可以从多个数据点返回数据。 - 与手动解析所需的开发时间相比,能够抓取原始 HTML 绝对是一个巨大优势。
缺点
- 与使用其他 SERP API 提供商相比,成本很高。
- 在传递整个原始 HTML 时要注意成本。我们仍然需要进行修剪 HTML,以便只抓取相关部分。否则,你必须为使用 token(口令)支付高额费用。.
- 将其用于生产时,速度太慢。
- 对于通常在脚本标签、额外的 AJAX 请求或执行操作(如点击、滚动)时发现的 “隐藏数据”,我们仍然需要手动操作。
工具和准备
- 由于我们要使用 OpenAI 的 API,因此请务必先注册并获得您的 api_key。您可能还需要 OpenAI 组织 ID。
- 我在这个实验中使用的是 Python,但你也可以随意使用任何编程语言。
- 由于我们希望返回统一的 JSON 格式,因此我们将使用 OpenAI 的函数调用功能,在这里我们可以用顺眼的格式定义响应的键和值。
- 我们将使用以下模型
gpt-4-1106-preview .
基础代码
确保先安装 OpenAI 库。由于我使用的是 Python,我需要
pip install openai我还将安装 requests 包,以获取原始 HTML 代码
pip install requests我们的代码库如下所示
import json
import requests
from openai import OpenAI
client = OpenAI(
organization='YOUR-OPENAI-ORG-ID',
api_key='YOUR-OPENAI-API-KEY'
)
targetUrl = 'https://books.toscrape.com/' # Target URL will always changes
response = requests.get(targetUrl)
html_text = response.text注:国内用户可能要设置 base_url,来使用代理或者第三方 API。
第 1 级:使用人工智能对漂亮/简单的结构化网页进行抓取
让我们先热热身。我们首先针对 https://books.toscrape.com/网站,因为它的结构非常简洁,便于阅读。
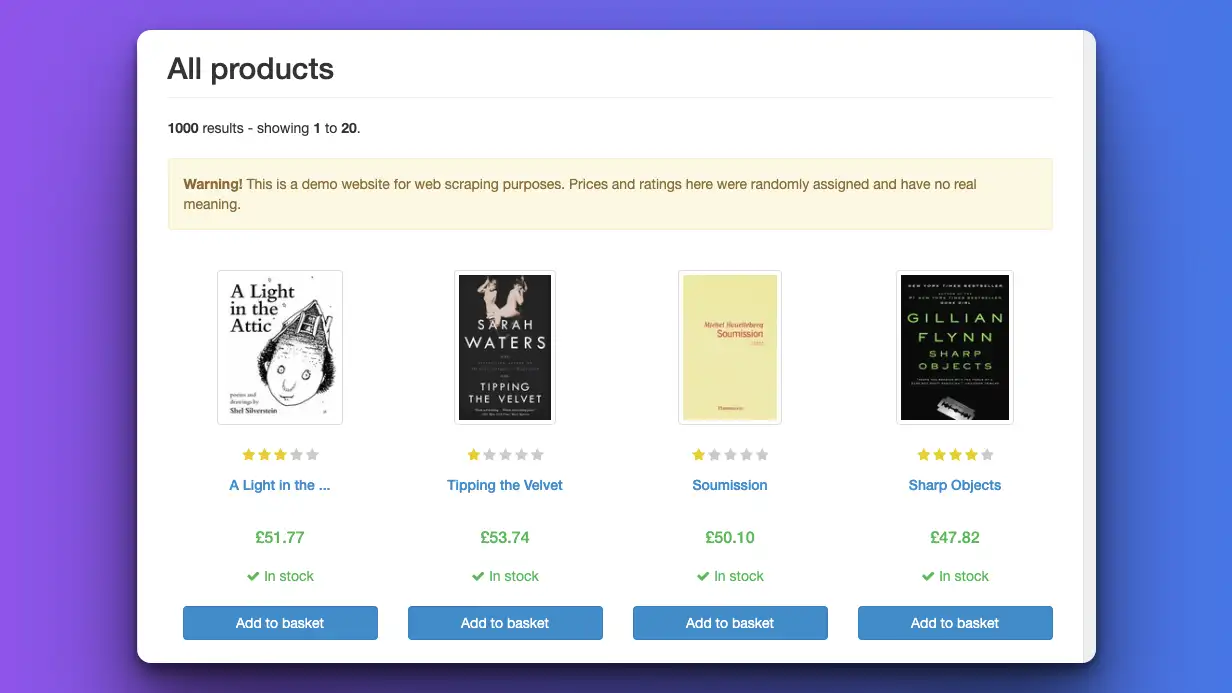
截图 toscrape books,是第一个网络抓取目标
下面是我们的代码(下面有解释)
# 来自 OpenAI 的 ChatCompletion API
completion = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4-1106-preview", # 请将模型改为 gpt-3.5-turbo-1106
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a master at scraping and parsing raw HTML."},
{"role": "user", "content": html_text}
],
tools=[
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "parse_data",
"description": "Parse raw HTML data nicely",
"parameters": {
'type': 'object',
'properties': {
'data': {
'type': 'array',
'items': {
'type': 'object',
'properties': {
'title': {'type': 'string'},
'rating': {'type': 'number'},
'price': {'type': 'number'}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
],
tool_choice={
"type": "function",
"function": {"name": "parse_data"}
}
)
# 数据结果的调用
argument_str = completion.choices[0].message.tool_calls[0].function.arguments
argument_dict = json.loads(argument_str)
data = argument_dict['data']
# 打印格式化
for book in data:
print(book['title'], book['rating'], book['price'])- 我们使用 OpenAI 的
ChatCompletionAPI - 使用模型: gpt-4-1106-preview
- 使用提示语
您是抓取和解析原始 HTML 的高手,并传递要分析的raw_html。 - 在
tools参数中,我们定义了用于解析原始数据的虚函数(imaginary function)。不要忘记调整参数的属性,以准确返回您想要的格式。
结果如下
我们可以抓取每本书的标题、评分和价格 _(正是我们在上述__函数参数中定义的数据)_。
运行完成时间: ~15s
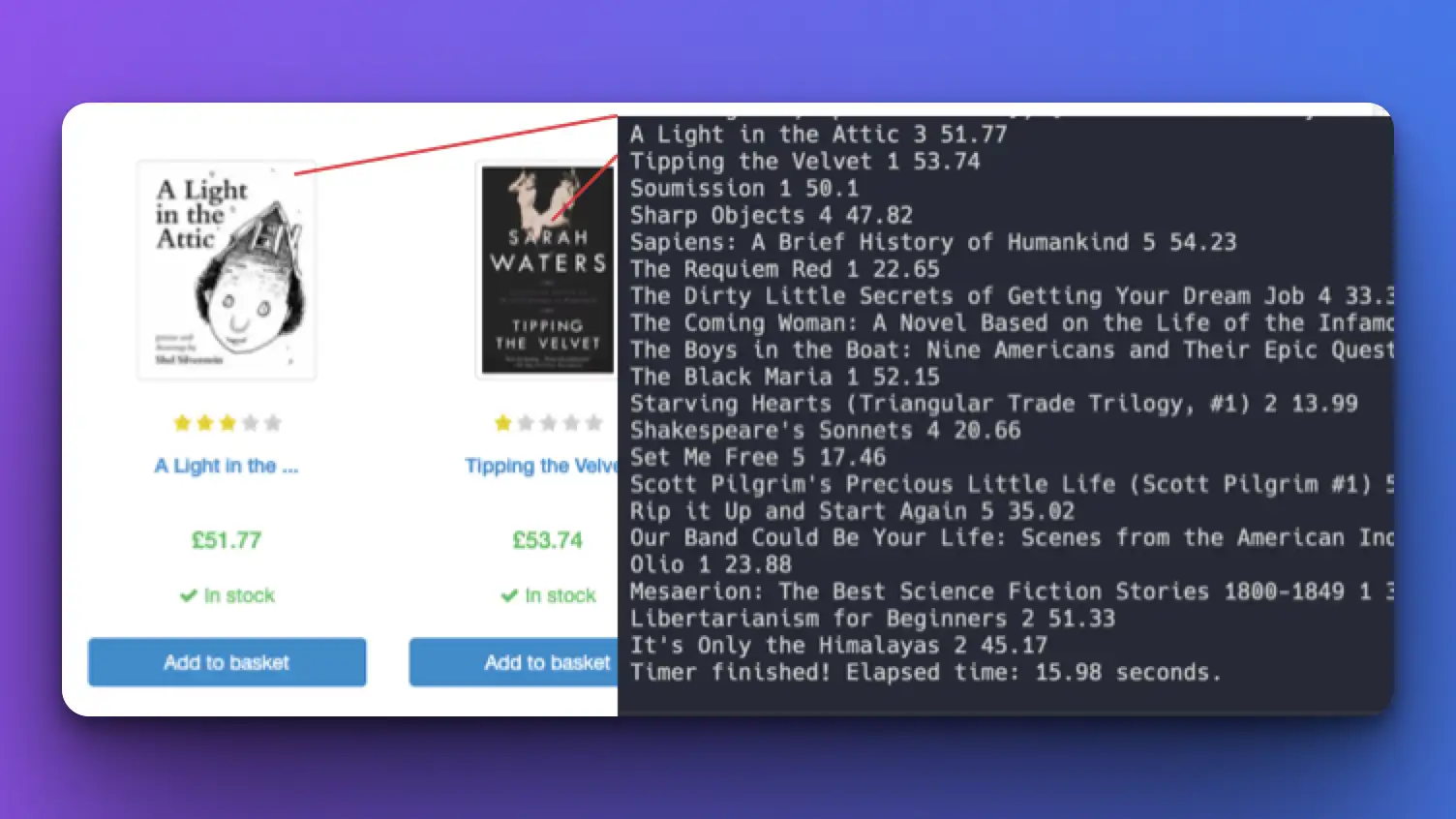
比较网络抓取结果
使用 gpt-3.5
当切换到 gpt-3.5-turbo-1106 时,我必须调整提示词,使其更加具体:
messages: {"role": "system", "content": "You are a master at scraping and parsing raw HTML. Scrape ALL the book data results"},
# function 描述
"function": {
"name": "parse_data",
"description": "Get all books data from raw HTML data",
}如果不提及 “抓取所有图书数据”,就只能得到前几个结果。
运行完成时间: ~9s
第 2 层:利用人工智能解析 Google SERP 中的自然搜索结果(Organic results)
谷歌搜索结果页面与之前的网站不同。它的结构更复杂,CSS 类名不清晰,原始 HTML 中包含许多未知数据。
目标 URL: ‘https://www.google.com/search?q=coffee&gl=us'
警告!起初,我只是解析 Google 原始 HTML 中的所有内容,结果发现其中包含太多字符,这意味着需要更多 token 和更多成本!
注意您的 OpenAI 账单使用情况
因此,在尝试了几次之后,我决定只要 body 部分,并删除 style 和 script 标记的内容。
我这样调整了提示词和功能参数:
import re #导入 regex
response = requests.get('https://www.google.com/search?q=coffee&gl=us')
html_text = response.text
# 删除不必要的部分,以避免巨额 TOKEN 费用!
# 删除 <head> 和 </head> 之间的所有内容
html_text = re.sub(r'<head.*?>.*?</head>', '', html_text, flags=re.DOTALL)
# 删除 <script> 和 </script> 之间出现的所有内容
html_text = re.sub(r'<script.*?>.*?</script>', '', html_text, flags=re.DOTALL)
# 删除 <style> 和 </style> 之间的所有内容
html_text = re.sub(r'<style.*?>.*?</style>', '', html_text, flags=re.DOTALL)
completion = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4-1106-preview",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a master at scraping Google results data. Scrape top 10 organic results data from Google search result page."},
{"role": "user", "content": html_text}
],
tools=[
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "parse_data",
"description": "Parse organic results from Google SERP raw HTML data nicely",
"parameters": {
'type': 'object',
'properties': {
'data': {
'type': 'array',
'items': {
'type': 'object',
'properties': {
'title': {'type': 'string'},
'original_url': {'type': 'string'},
'snippet': {'type': 'string'},
'position': {'type': 'integer'}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
],
tool_choice={
"type": "function",
"function": {"name": "parse_data"}
}
)
argument_str = completion.choices[0].message.tool_calls[0].function.arguments
argument_dict = json.loads(argument_str)
data = argument_dict['data']
for result in data:
print(result['title'])
print(result['original_url'] or '')
print(result['snippet'] or '')
print(result['position'])
print('---')- 首先,我们只修剪(trim)选中的部分。
- 将提示词调整为
您是 Google 搜索结果数据的高手。从 Google 搜索结果页面抓取前 10 条自然搜索结果数据(You are a master at scraping Google results data. Scrape top 10 organic results data from Google search result page.)。 - 将功能参数调整为所需的格式。
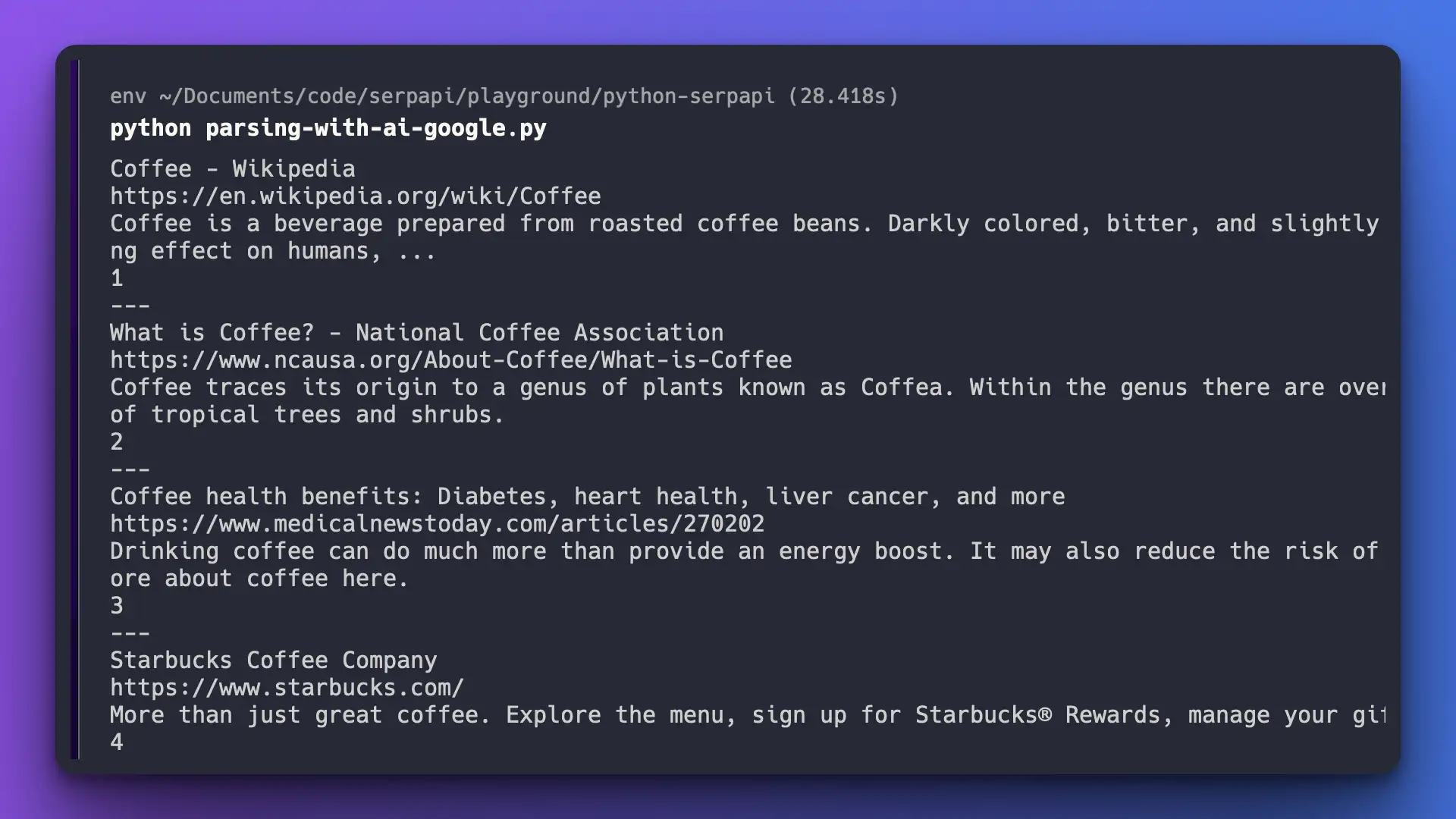
利用人工智能对谷歌 SERP 进行基本的网络抓取
哒哒哒!尽管谷歌原始 HTML 格式复杂,我们还是准确地获得了所需的数据。
运行完成时间: ~28s
备注: 我最初的提示词是
很好地解析 Google SERP 原始 HTML 数据中的自然搜索结果(Parse organic results from Google SERP raw HTML data nicely),但只能返回前 3-5 个结果,因此我调整了提示词,以获得更多的结果。
使用 gpt-3.5 模型
我无法做到这一点,因为原始 HTML 数据量超过了 token 窗口长度。
第 3 层:利用人工智能解析谷歌地图中的本地地点结果
现在,让我们抓取另一个 Google 产品,即 Google 地图。这是我们的目标页面: https://www.google.com/maps/search/coffee/@40.7455096,-74.0083012,14z?hl=en&entry=ttu
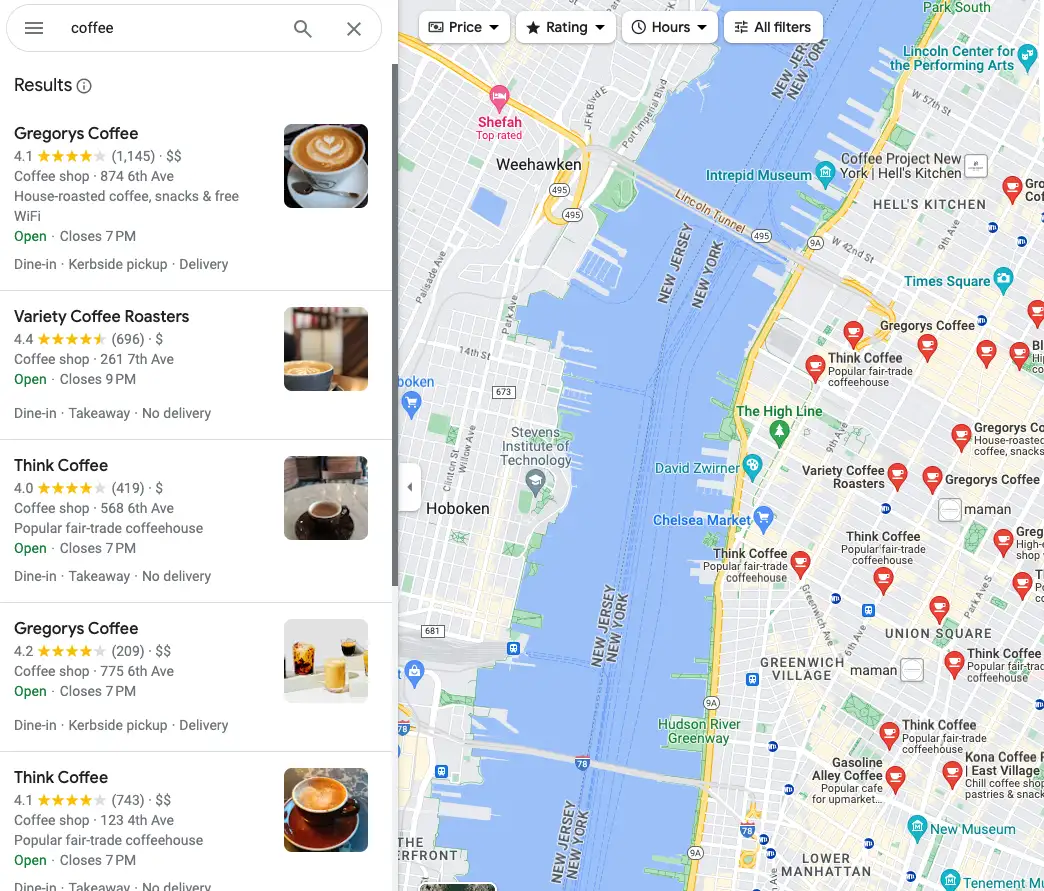
谷歌地图截图
如您所见,每个项目都包含许多信息。我们将进行搜索:
- Name
- Rating average
- Total rating
- Price
- Address
- Extras
- Hours
- Additional service
- Thumbnail image
警告! 原来,谷歌地图是通过 Javascript 来加载这些数据的,所以我必须改变获取原始网页的方法,从使用
requests改为使用selenium来获取
代码
在 Python 上安装 Selenium。更多安装说明请参阅 此处。
pip install selenium导入 Selenium
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.common.keys import Keys
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By创建一个无头浏览器实例来浏览网页
target_url = 'https://www.google.com/maps/search/coffee/@40.7455096,-74.0083012,14z?hl=en'
op = webdriver.ChromeOptions()
op.add_argument('headless')
driver = webdriver.Chrome(options=op)
driver.get(target_url)
driver.implicitly_wait(1) # seconds
# 获取的原始网页
html_text = driver.page_source
# 您可以继续使用之前的方法,先只修剪 body 部分我使用 implicitly_wait 等待 1 秒钟,以确保数据已经在那里,可以进行抓取。
下面是 OpenAI API 函数:
completion = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4-1106-preview",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a master at scraping Google Maps results. Scrape all local places results data"},
{"role": "user", "content": html_text}
],
tools=[
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "parse_data",
"description": "Parse local results detail from Google MAPS raw HTML data nicely",
"parameters": {
'type': 'object',
'properties': {
'data': {
'type': 'array',
'items': {
'type': 'object',
'properties': {
'position': {'type': 'integer'},
'title': {'type': 'string'},
'rating': {'type': 'string'},
'total_reviews': {'type': 'string'},
'price': {'type': 'string'},
'type': {'type': 'string'},
'address': {'type': 'string'},
'phone': {'type': 'string'},
'hours': {'type': 'string'},
'service_options': {'type': 'string'},
'image_url': {'type': 'string'},
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
],
tool_choice={
"type": "function",
"function": {"name": "parse_data"}
}
)
argument_str = completion.choices[0].message.tool_calls[0].function.arguments
argument_dict = json.loads(argument_str)
data = argument_dict['data']
print(data)结果
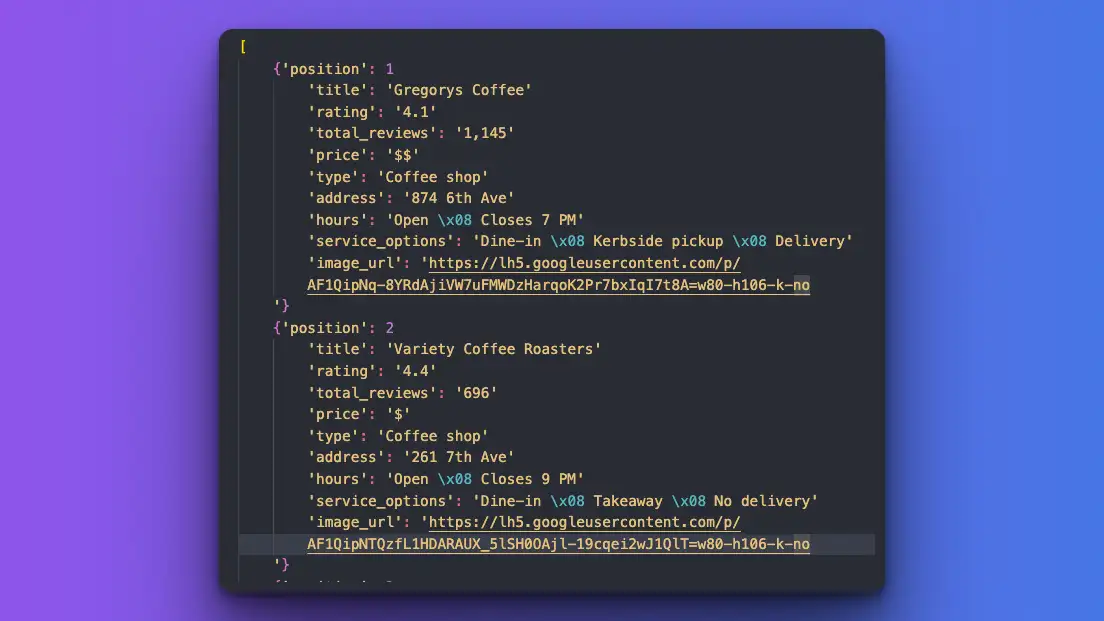
利用人工智能进行本地地图 API 搜索的结果
结果很完美!我可以获得每个 local_results 的准确数据。
运行完 Selenium 时间: ~47s
运行时间 (除了 Selenium ): ~34s
第 4 层次: 利用人工智能解析来自 Google SERP 的两种不同数据(自然搜索结果和人们询问相关问题的部分)
如您所知,谷歌 SERP 不仅显示自然搜索结果,还显示其他数据,如广告、people-also-ask(相关问题)、知识图谱等。
让我们来看看如何利用调用 OpenAI 的多个函数处理多个数据。
代码如下
completion = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4-1106-preview",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a master at scraping Google results data. Scrape two things: 1st. Scrape top 10 organic results data and 2nd. Scrape people_also_ask section from Google search result page."},
{"role": "user", "content": html_text}
],
tools=[
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "parse_organic_results",
"description": "Parse organic results from Google SERP raw HTML data nicely",
"parameters": {
'type': 'object',
'properties': {
'data': {
'type': 'array',
'items': {
'type': 'object',
'properties': {
'title': {'type': 'string'},
'original_url': {'type': 'string'},
'snippet': {'type': 'string'},
'position': {'type': 'integer'}
}
}
}
}
}
}
},
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "parse_people_also_ask_section",
"description": "Parse `people also ask` section from Google SERP raw HTML",
"parameters": {
'type': 'object',
'properties': {
'data': {
'type': 'array',
'items': {
'type': 'object',
'properties': {
'question': {'type': 'string'},
'original_url': {'type': 'string'},
'answer': {'type': 'string'},
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
],
tool_choice="auto"
)
# Organic_results(自然搜索结果)
argument_str = completion.choices[0].message.tool_calls[0].function.arguments
argument_dict = json.loads(argument_str)
organic_results = argument_dict['data']
print('Organic results:')
for result in organic_results:
print(result['title'])
print(result['original_url'] or '')
print(result['snippet'] or '')
print(result['position'])
print('---')
# People also ask (相关问题)
argument_str = completion.choices[0].message.tool_calls[1].function.arguments
argument_dict = json.loads(argument_str)
people_also_ask = argument_dict['data']
print('People also ask:')
for result in people_also_ask:
print(result['question'])
print(result['original_url'] or '')
print(result['answer'] or '')
print('---')代码说明
- 调整提示词,使其包含关于抓取内容的具体信息:
您是搜索 Google 结果数据的高手。搜索两样东西: 第一。抓取排名前 10 的自然搜索结果数据;第二。从 Google 搜索结果页面中抓取 _the_ people_also_ask 部分(You are a master at scraping Google results data. Scrape two things: 1st. Scrape top 10 organic results data and 2nd. Scrape the _the_ people_also_ask section from the Google search result page)。 - 添加并分离函数(separating functions),一个用于自然搜索结果,另一个用于 people-also-ask 部分。
- 测试两种不同格式的输出。
结果如下:
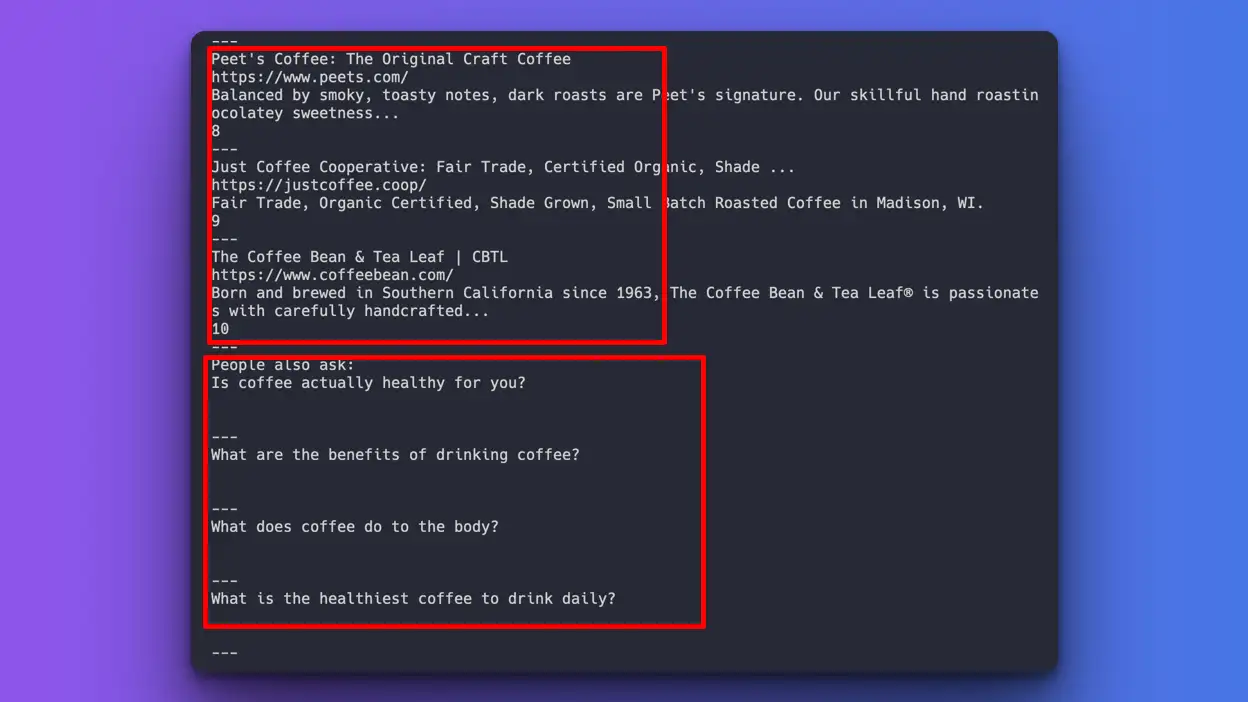
利用人工智能获取多个数据点
成功
我可以分别搜索自然搜索结果和 people_also_ask。OpenAI 功不可没!
问题:
我无法为 people_also_ask 部分提取答案和原始网址。原因是这些信息隐藏在脚本标签的某处。我们可以通过提供脚本内容的特定部分来尝试,但我认为这对本实验来说是 作弊,因为我们要传递的是原始网页内容,而不是精确定位或给出提示。
运行时间: ~30s
如果您想了解如何更低代价、更快速、更准确地搜索这些数据。您可以阅读以下文章:
与 SerpApi 的表格比较
以下是使用 OpenAI 新的 GPT-4 模型进行网络抓取与SerpApi的时间表对比。我们使用 正常速度 进行比较;SerpApi 在使用Ludicrous Speed时速度更快(大约是正常速度的两倍)。
| Subject | gpt-4-1106-preview | SerpApi |
|---|---|---|
| Organic results | 15s | 2.4s |
| Organic results with Related questions | 30s | 2.4s |
| Maps local results | 47s | 2.7s |
结语
随着时间的推移,OpenAI 肯定会有很大改进。现在,我们可以通过应用程序接口(API)抓取网站并收集相关数据。但从所花费的时间来看,它还不能用于生产、商业目的或规模化。虽然数据的准确性和响应格式都很完美,但在成本和速度方面还远远不够。
如果您有任何想法、发现任何错误,或想补充与本文章相关的其他实验,请发送邮件至 [email protected]。
感谢您阅读此文!





